Mapping relative differences in belowground biomass in wetlands
 Wednesday, December 2, 2015 at 8:00PM
Wednesday, December 2, 2015 at 8:00PM O’Connell, JL, KB Byrd, and M Kelly. 2015. A Hybrid Model for Mapping Relative Differences in Belowground Biomass and Root:Shoot Ratios Using Spectral Reflectance, Foliar N and Plant Biophysical Data within Coastal Marsh. Remote Sensing 7, 16480-16503
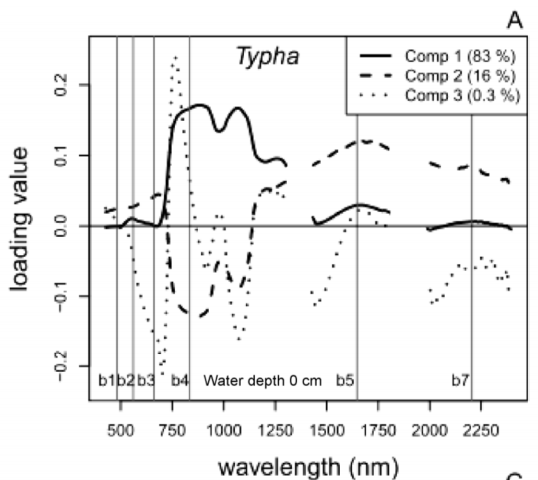 Loadings values of % foliar N from PLS regression of hyperspectral data for Typha spp. Broad-scale estimates of belowground biomass are needed to understand wetland resiliency and C and N cycling, but these estimates are difficult to obtain because root:shoot ratios vary considerably both within and between species. We used remotely-sensed estimates of two aboveground plant characteristics, aboveground biomass and % foliar N to explore biomass allocation in low diversity freshwater impounded peatlands (Sacramento-San Joaquin River Delta, CA, USA). We developed a hybrid modeling approach to relate remotely-sensed estimates of % foliar N (a surrogate for environmental N and plant available nutrients) and aboveground biomass to field-measured belowground biomass for species specific and mixed species models.
Loadings values of % foliar N from PLS regression of hyperspectral data for Typha spp. Broad-scale estimates of belowground biomass are needed to understand wetland resiliency and C and N cycling, but these estimates are difficult to obtain because root:shoot ratios vary considerably both within and between species. We used remotely-sensed estimates of two aboveground plant characteristics, aboveground biomass and % foliar N to explore biomass allocation in low diversity freshwater impounded peatlands (Sacramento-San Joaquin River Delta, CA, USA). We developed a hybrid modeling approach to relate remotely-sensed estimates of % foliar N (a surrogate for environmental N and plant available nutrients) and aboveground biomass to field-measured belowground biomass for species specific and mixed species models.