Finding trees in the lidar point cloud
 Friday, January 20, 2012 at 9:47AM
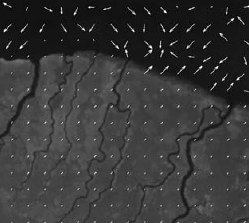
Friday, January 20, 2012 at 9:47AM  individual trees extracted from the lidar point cloudLi, W., Q. Guo, M. Jakubowski and M. Kelly. 2012. A new method for segmenting individual trees from the lidar point cloud. Photogrammetric Engineering and Remote Sensing 78(1): 75-84
individual trees extracted from the lidar point cloudLi, W., Q. Guo, M. Jakubowski and M. Kelly. 2012. A new method for segmenting individual trees from the lidar point cloud. Photogrammetric Engineering and Remote Sensing 78(1): 75-84
In this study we develop a new algorithm to segment individual trees from the small footprint discrete return airborne lidar point cloud. The new algorithm adopts a top-to-bottom region growing approach that segments trees individually and sequentially from the tallest to the shortest. We experimentally applied the new algorithm to segment trees in a mixed coniferous forest in the Sierra Nevada Mountains in California, USA. Our results indicate that the proposed algorithm has good potential in segmenting individual trees in mixed conifer stands of similar structure using small footprint, discrete return lidar data.
 forests,
forests,  lidar,
lidar,  obia,
obia,  remote sensing,
remote sensing,  snamp,
snamp,  sugar pine
sugar pine